Introduction
There are some most rare diseases in the world that are talked about in this blog post. We’re going to talk about their problems, signs, and makes sense. Health professionals are interested in both diseases that happen often and diseases that don’t happen very often. They will also show you how important it is to study medicine and help people who are sick. Let’s find out more about these cool, rare illnesses.
Understanding the most rare diseases in the world
There is a complex of most rare diseases in the world, which is often misunderstood.Even though these disorders only affect a tiny number of people, they can have a big effect on the lives of those who are diagnosed with them. To help people who have rare diseases and their families, it is important to know what they are and how they affect people.
Definition of most rare diseases in the world
When fewer than 200,000 people in the United States suffer from a rare disease, it is classified as such. The definitions may vary internationally, but the focus remains on low prevalence and the significant challenges they present in diagnosis and treatment.
Prevalence and Classification
There are considered to be about 7,000 rare diseases, and most rare diseases in the world only affect a few people. Researchers and doctors usually use the symptoms, genetic origins, and the organ systems that are affected to find out what diseases are and how to treat them.
There are a number of rare diseases, and many of them have things in common that set them apart from other diseases. For example, their symptoms could be very complicated or they could get worse over time. It can be hard to find solid statistics for this disease because it is so rare. Many individuals still don’t realize they have it or have been told they have it wrong, which shows how important it is to tell others about it and teach them about it.
Genetic and Acquired Diseases
To understand most rare diseases in the world better, you need to know the distinction between inherited and acquired disorders. A genetic unusual disease results from alterations in DNA, whereas an acquired disease arises from pathogens or environmental factors.
This difference is very crucial to understand. Genetic illnesses affect individuals regardless of environmental factors, whether inherited or resulting from spontaneous mutations. Acquired diseases, however, occur postnatally and may result from factors such as lifestyle choices, infections, or exposure to hazardous substances. Recognizing these disparities lets you tailor prevention and treatment methods.
Notable Most Rare Diseases in the World
Most rare diseases in the world cannot be discussed without mentioning some of the most notable conditions that affect a small percentage of the population. Those diagnosed with these diseases as well as healthcare professionals trying to provide proper care and support often face unique challenges.
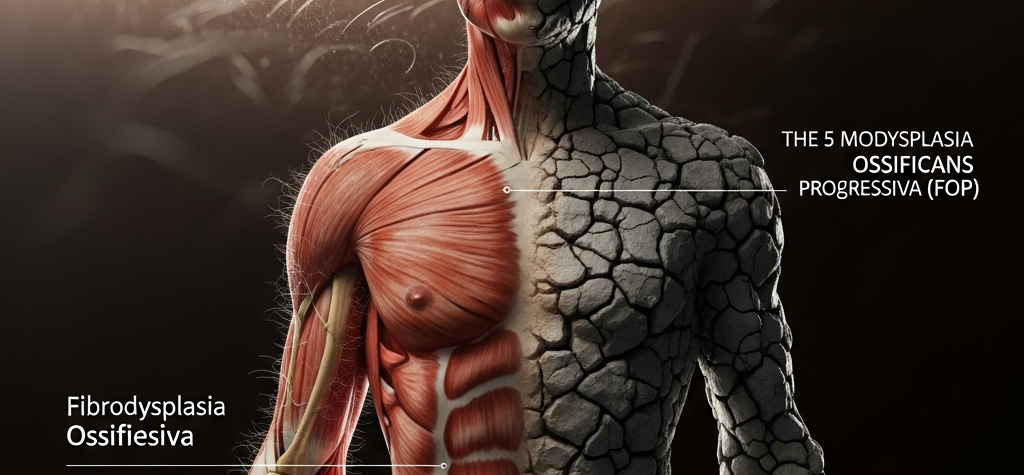
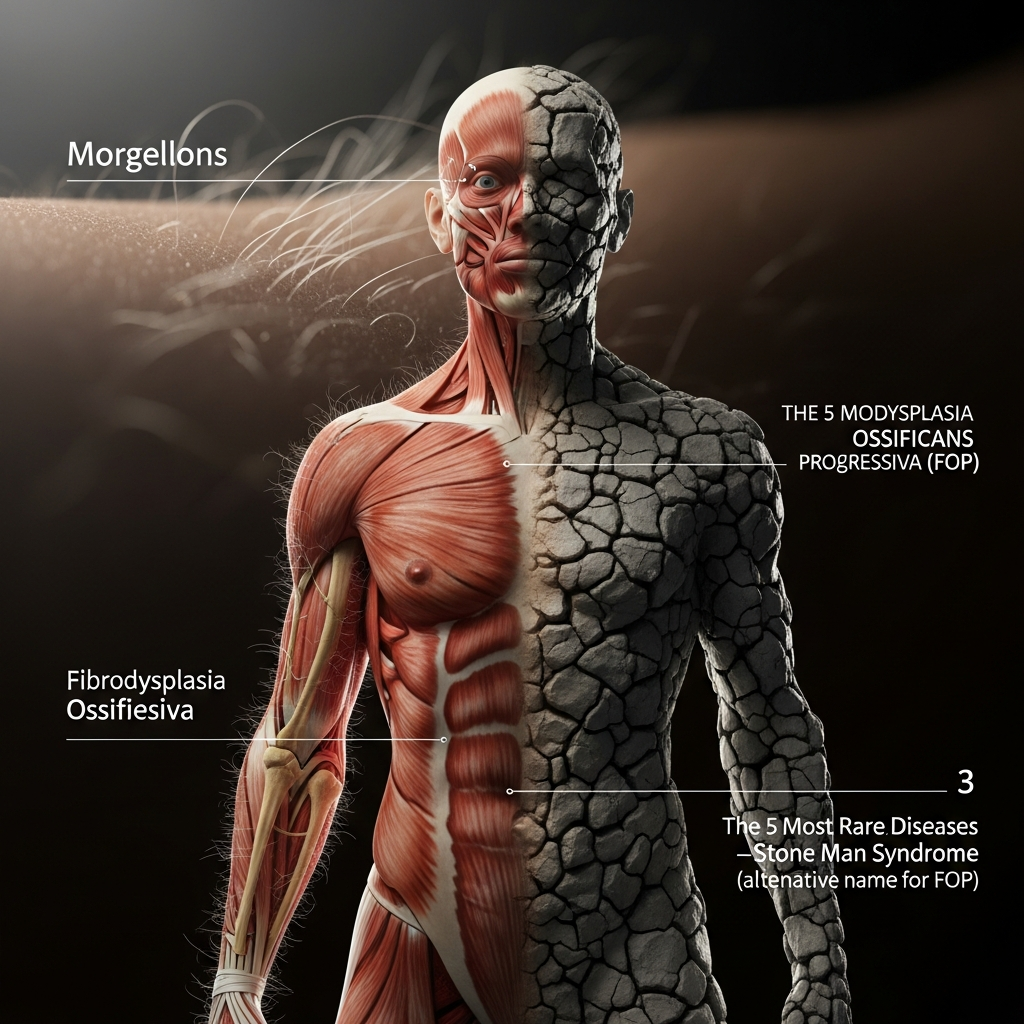
1. Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP)
People with Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP) slowly lose their ability to form bones. Because of this, they need to have a second skeleton created. This uncommon connective tissue disease can make it hard to move and impair your quality of life when new bone forms in the wrong place, which often happens after an accident or inflammation.
2. Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS)
Progressive Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS) is a rare neurological disorder that makes it hard to move because your muscles are stiff and spasm. Patients may experience severe muscle rigidity, aggravated by stress or incidental stimulation, hindering the performance of daily activities.
People with Stiff Person Syndrome frequently have a number of various symptoms, like anxiety and being more sensitive to stimuli. These symptoms make the stiffness and spasms in the muscles worse. It is considered that people with this disease have an autoimmune illness, which means that their immune system attacks their own tissues in the wrong way. A mix of medicines and physical therapy is the most common technique to treat this. It helps with symptoms and movement.
3. Ondine’s Curse (Congenital Hypoventilation Syndrome)
People may be able to breathe normally when they’re awake, but they may have trouble doing so while they sleep. They might not be able to breathe if this isn’t watched.
A big part of the problem is that while you sleep, your brain can’t tell the difference between low oxygen and high carbon dioxide. Some people need ventilators or extra air because of this. There aren’t enough words to describe how important early diagnosis is. It makes treatment plans better and, with the right help, lets people live more busy lives.
4. Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome(HGPS)
A very rare genetic disorder called childhood progeria accelerates the aging process. Although they are typically considered healthy at birth, infants with Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS) will exhibit symptoms such as hair loss, delayed growth, and cardiovascular problems when they age too fast.
Gilford and Hutchinson A mutation in the LMNA gene causes abnormal protein synthesis and cell damage, which leads to Progeria Syndrome. Despite having a significantly shorter life expectancy, the majority of affected individuals live into adolescence, but recent research is raising hopes for medications that could improve quality of life.
5. Fields Syndrome
Hypoventilation is associated with a rare and complex disorder known as Fields Syndrome. This syndrome is caused by problems with thinking, moving, and perceiving that all happen at the same time. These issues could make it tougher for a child to grow up.
People who have Ondines syndrome often have lung difficulties that make it hard to breathe and make breathing problems worse.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of a lot of the world’s rare diseases Finding it can be hard, but early discovery can help a lot of people with rare conditions. It might be hard to tell the difference between the symptoms of rare diseases and those of more common ones, which can lead to wrong or late diagnoses. To find these diseases early, it’s important to know what symptoms they show.
Common Symptoms of Rare Diseases
The symptoms and signs of rare diseases that people around the world see most often. A lot of the time, people have a set of signs that can be very different from one person to the next. Some of these signs are being tired in a way that doesn’t make sense, being physically weak, having trouble thinking, or skin changes. So it’s hard to tell these signs apart from more common ones. This makes it harder to find a rare disease.
Having Trouble Diagnosing
The problems with identifying rare diseases: How hard it is to diagnose the world’s strangest diseases. Some rare diseases are hard to spot because they don’t happen very often and don’t have clear signs.
Doctors use patient histories, a list of all their symptoms, and talks with experts to figure out how to treat these issues. As a general rule, you should find out as soon as possible what illnesses someone has. You might make things worse and find good solutions if you wait too long to find out. Doctors and hospitals don’t know much about rare diseases, which makes it even harder to find and treat them quickly.
The Purpose of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing provides many patients with definitive answers by identifying mutations associated with specific rare diseases. When other diagnostic techniques are unsuccessful, this approach can occasionally be quite beneficial. Physicians can provide patients with more direction and create more individualized treatment strategies by using genetic markers. Genetic testing helps people better comprehend diagnoses in addition to confirming them. It makes it easier to treat and manage rare disorders.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of most rare diseases in the world. IWhile medical science is slowly changing the landscape of rare diseases, there are no established cures for many of them.
Available Treatments for Rare Diseases
Treatment of rare diseases : Individual symptoms may require different treatment pathways for different diseases. The rare nature of many rare diseases necessitates the use of off-label medications, supportive therapies, or disease-specific interventions intended to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
The Importance of Clinical Trial
This is because science has grown a lot. People who take part in these trials get to try out new drugs and also help with important research that will help make medicines better in the future.
Emeging Therapies an Resarch
Research finds innovative ways to treat some of the world’s most uncommon diseases. More and more new treatments are showing that there might be new approaches to help people with uncommon diseases. There are a lot of new ideas that could transform how you cope with long-term health problems. Some of these are gene therapy, biologics, and personalized medicine.
It is really important to keep doing research on a topic. By researching the genetics and mechanics of uncommon diseases, scientists will be able to create medicines that work for such disorders. This will help people like you get better results and give hope for better ways to treat rare diseases in the future.
Impact on Patients and Families
A rare disease can have a huge and difficult influence on the individual who has it and their family. They can also influence how people feel and what they do every day. Effects on the mind and feelings
Psychological and Emotional Effects
People who have rare diseases often experience mental health concerns. This emotional weight can make relationships tense and make life less enjoyable.
Economic Effects of Rare Diseases
The financial impact of a rare disease can be overwhelming for many families. It is not unusual for medical treatments, medications, and ongoing care to cost a great deal of money.
Help for Families Who Are Affected
Help for families with one of the world’s most uncommon diseases. People with rare diseases and their families often ask for help dealing with the problems that come with having one. Support organizations, advocacy groups, and websites with information can help you with your problems and give you emotional support.
Families can obtain a lot of help and understanding from people who have been through the same thing. There are also many groups and charities that can help you pay for goods, learn more about your illness, and take part in clinical trials.
Advocacy and Awareness
More people talking about strange illnesses will help us understand them better and help those who have them. These groups feel strong when they see, hear, and teach people who have rare diseases.
Role of Non-Profit Organizations
People who give to these groups believe they are very important. These groups can help sick people and teach them important things about health. They work with doctors and other experts to get better care and get the word out about illnesses that not many people know about.
Day of Awareness for Rare Diseases and the Community
Tomorrow, people should think about how hard it is for sick people who are rare. Every year, people from all over the world come to this event to meet new people, share their stories, and fight for better tools.
People learn more than just how to get sick during public health campaigns. When more people learn about uncommon diseases on Uncommon Disease Day, the shame that comes with having one goes away. They will make things better for people in the long run.
Legislative Efforts and Policy Changes
There are NOV groups that want to change the rules in ways that could make your area very different.
What’s next for AI and data analytics in rare diseases?
Data analysis has let us see rare diseases in a new light. As AI gets better, it should be easier to find likely drug options and guess how patients will respond to treatment. AI and data analytics will help you put your data together in a better way. This new method can make it easier and faster to find and treat rare diseases. How well future patients do will depend on how you act in this changing climate.
Conclusion
Taking a look at the most rare diseases in the world highlights the importance of understanding and raising awareness about these conditions. As you gain knowledge about rare diseases, you empower yourself and others to advocate for improved research, treatment options, and support systems for those who suffer from them.
Related Posts
- Life Expectancy With Fatty Liver Disease
- 4 Best Exercises for Health
- 4 Holistic Approaches to Managing Chronic Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Science of Shedding Pounds: A Data-Driven Approach to Weight Loss
- 3 Top Risk Factors of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva in Newborn
- Home



































































































