Introduction
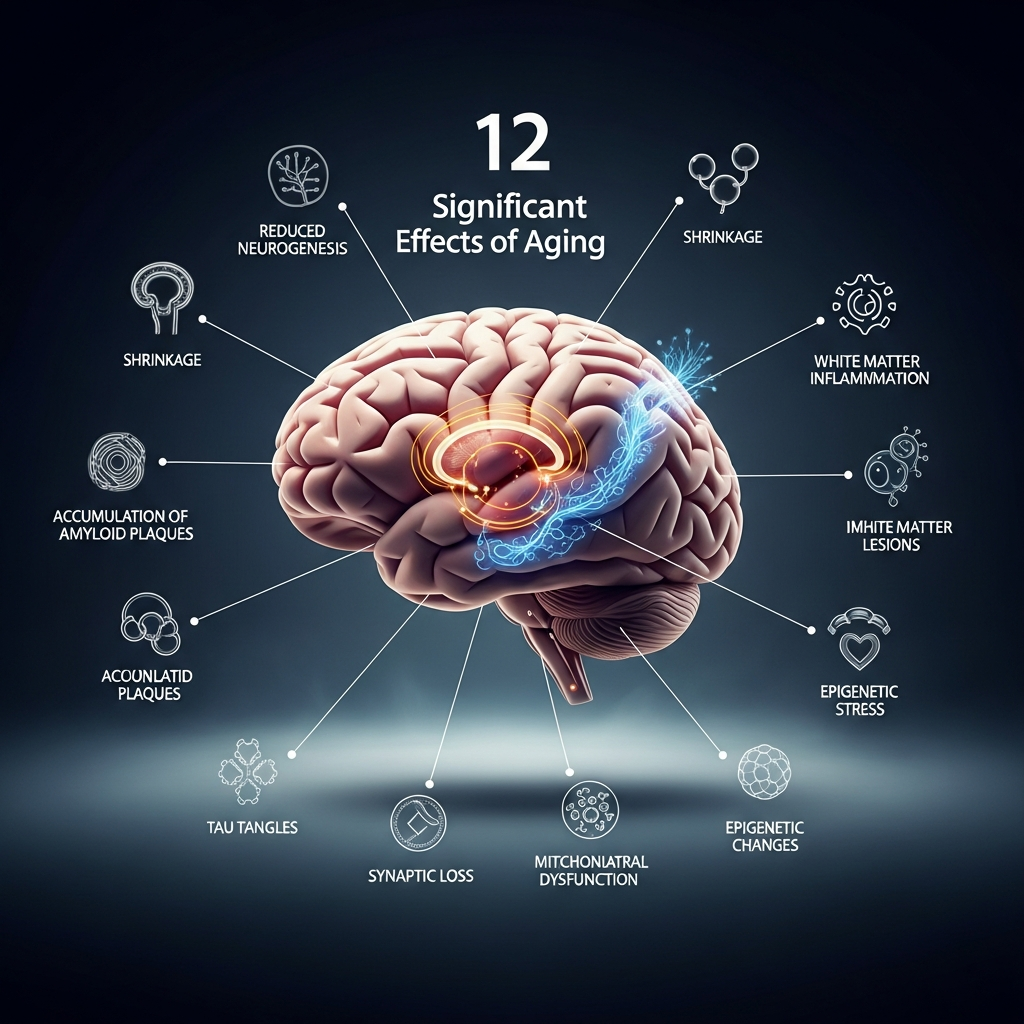
This blog post will talk about 12 significant aging effects on the brain. as we age. A lot of information is out there about how brains change as people age.
You might be able to keep your brain healthy in the future if you know about these benefits. Researchers have found that the changes that happen to our bodies as we age can impact not only our memory and thinking skills but also how we think and remember things. We’ll look 12 significant aging effects on the brain in this blog post. We want to give you ideas that will help you stay mentally sharp and healthy for a long time.
Understanding the Aging Effects on the Brain
It should be mentioned that aging effects on the brain impacts all of your body’s organs, including the brain, and is a normal aspect of life. Understanding how the brain develops with age is essential to maintaining cognitive health and well-being. In this section, we’ll cover a wide range of subjects, such as the aging process, the anatomy of the brain, and some important vocabulary that will help you better understand how aging impacts the brain.
The Brain’s Anatomy and Functions
Some people say that the brain is one of the most difficult parts of the body. It has over 86 billion neurons that control things like feeling, moving, and remembering. The brain is made up of different parts that work together to shape how you think and live. To fully understand how getting older changes the body’s main processes, you need to know about the parts that are involved.
Overview of Aging Process
As you age, your brain changes a lot about how it looks and how it works. As you age, your brain will have fewer synapses and the connections between them will not work as well. It will make your brain hurt. How fast aging effects on the brain. can also be changed by your genes, health problems, and the way you live your life.
This kind of decline often makes people think more slowly, remember things less clearly, and have other mental issues. It’s true that getting older can be bad, but keep in mind that not everyone does forget things as they get older. If you eat well and do things that make your mind work, some of these benefits may be lessened and your brain health may get better.
Key Terminology in Brain Aging
Certain concepts are crucial to comprehending the aging process of the brain as it ages. When it comes to aging effects on the brain, cognitive reserve, neuroplasticity, and dementia are frequently discussed, and these concepts are frequently employed in these talks. As you get more comfortable with the following ideas, you’ll be able to negotiate the complexity of brain aging more effectively.
Understanding terminology and anatomy is essential to comprehending how aging effects on the brain function. In the field of neuroscience, the ability of the brain to change and develop new connections as an adult is known as neuroplasticity, and the ability of the brain to adapt to aging-related changes is known as cognitive reserve. Having a thorough understanding of these fundamental ideas can help you make more informed decisions regarding your brain’s health as you mature.
Cognitive Decline
Cognitive decline, a term used to describe a variety of changes in your mental capacities as you age, is one of the most obvious impacts of aging effects on the brain
. Memory, processing speed, and problem-solving skills are just a few of the cognitive talents that might deteriorate with age due to a variety of circumstances.
Memory Loss
The main aging effects on the brain is memory loss. Senior citizens are more prone to suffer from some degree of memory loss as they get older. This can show up as problems remembering names, losing track of where you put items, or experiencing memory loss related to recent conversations. It’s crucial to continue doing memory-boosting activities like reading and solving puzzles because occasional forgetfulness is a common occurrence.
Impaired Problem-Solving Skills
Impaired problem is one of the aging effects on the brain. Age-related declines in problem-solving abilities are another possibility. This implies that you can find it challenging to solve common problems or to come to judgments quickly.
Playing strategy games or picking up new skills are two things that can help with this disability because they call for critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. You can build resilience against cognitive decline and improve your general mental agility by regularly pushing your brain and immersing yourself in tough tasks.
Neuroplasticity and Aging
Understanding how neuroplasticity plays a critical part in sustaining cognitive function as aging effects on the brain throughout one’s lifespan is vital to understanding the myriad facets of aging.
Definition of Neuroplasticity
In essence, neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself throughout life in order to form new neural connections when it encounters new situations. Your brain is a highly flexible organ that can swiftly learn new abilities, adapt to unfamiliar circumstances, and recover from injuries.
Impact of Aging on Neuroplasticity
The aging effects on the brain is neuroplasticity. In essence, neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself throughout life in order to form new neural connections when it encounters new situations. Your brain is a highly flexible organ that can swiftly learn new abilities, adapt to unfamiliar circumstances, and recover from injuries.
Neurochemicals that support neuroplasticity, notably brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), typically decline with age. As a result, memory loss and slower cognitive processing rates are common in elderly persons. That being said, it is important to keep in mind that neuroplasticity is a dynamic process and does not entirely vanish. By taking part in mentally stimulating activities, you can preserve some degree of cognitive resilience far into old age.
Strategies to Enhance Neuroplasticity in Older Adults
Regularly engaging in activities that challenge your mind and body is an excellent technique for slowing the effects of aging on the brain’s neuroplasticity. When you overcome a hurdle or learn a new ability, your brain might form new connections.
This all-encompassing neuroplasticity development model tries to encourage people to engage in cognitive work and physical activity while also valuing social connection and physical activity. A well-balanced lifestyle that fosters both physical and mental health can make it easier to adapt to new situations. It is critical to maintain your curiosity and activity as you age in order to keep your brain sharp.
Neurological Disorders Related to Aging
The aging effects on the brain is neurological disorders. For example, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases are not unavoidable aspects of aging. They are not the product of aging, despite the widespread misunderstanding of aging. Instead, they are a collection of intricate circumstances that may profoundly affect your life’s quality. It’s critical to recognize these conditions as you become older so you can take preventative measures to keep your brain healthy.
Alzheimer’s Disease: It is imperative to include this condition in any conversation about aging and the brain. This illness has a number of early symptoms, including disorientation and amnesia, which often appear gradually over time. Without a doubt, when the illness worsens, it can significantly affect day-to-day functioning. For this reason, it is critical to identify symptoms early in order to take appropriate action.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, which causes stiffness, trembling, and difficulty maintaining balance. As the illness progresses, cognitive function may suffer, making it more difficult to recall and complete tasks.
It’s crucial to understand that Parkinson’s disease affects more than just your physical health. It may also create mood swings and make it difficult to carry out daily activities. Early warning symptoms, such as minor shaking or changes in how you move, can assist doctors in determining what is wrong and may even improve your quality of life.
Vascular Dementia
Parkinson’s disease is caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, which causes stiffness, trembling, and difficulty maintaining balance. As the illness progresses, cognitive function may suffer, making it more difficult to recall and complete tasks.
It’s crucial to understand that Parkinson’s disease affects more than just your physical health. It may also create mood swings and make it difficult to carry out daily activities. Early warning symptoms, such as minor shaking or changes in how you move, can assist doctors in determining what is wrong and may even improve your quality of life.
Emotional and Social Effects of Aging
Aging has an effect on all facets of a person’s life throughout time, including the development of social networks and emotional control. Without a doubt, the changes that come with aging can have a big impact on your overall wellness and quality of life.
Changes in Emotional Regulation
Over the course of your life, you could observe changes in the way your emotional control functions. Over time, your capacity to handle life’s ups and downs may either get better or worse, which could mean that you become more sensitive to emotions or that it gets harder for you to handle difficult situations.
Impact on Social Interactions
Without a question, social connection gets more and more crucial as you get older, but it also undergoes major changes. It could be that you are observing a shift in the way you engage with people; certain friendships might be vanishing while new ones are forming, which could have a beneficial impact on your sense of community.
A decline in social relations can result from aging for a variety of reasons, including retirement, problems with mobility, or the death of a loved one. You may notice that your social networks are getting smaller and your friendships are fading, and you may start to feel alone or lonely. Participating actively in social events is essential to preserving a sense of fulfillment and equilibrium since it can support the maintenance of relationships that support emotional equilibrium.
Mental Health Considerations
One of the most important parts of aging is mental health because as you age, you may experience problems like anxiety and depression more often. In order to get support and maintain your mental health going forward, you must be able to identify these emotions.
When it comes to aging and mental health, a lot of variables may interact. Mental health problems can be caused by a variety of things, such as significant life changes, loved one death, and cognitive deterioration. The secret to managing the emotional terrain of aging more skillfully is to place a high priority on mental wellness through hobbies, maintaining social connections, and getting help from professionals when required. This improves your ability to manage the negative impacts of aging on your mental well-being.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Brain Aging
I want to stress again how important lifestyle decisions are in how your brain ages and how you can keep it from growing worse. Your daily activities have the power to either accelerate or decelerate the aging process’s effects on cognition. A multitude of lifestyle factors are known to influence brain aging, with some of the more significant ones being as follows:
- Nutrition
- Physical activity
- Sleep quality
- Stress management
- Cognitive engagement
- Social interaction
This demonstrates to us the significance of being aware of how our decisions affect the health of our brains.
Nutrition and Brain Health
It is true that aging has an impact on how well your brain functions, but some of these effects can be lessened by diet.
The Role of Technology in Aging Brain Research
Neuroscience and AI will help us understand the brain better over time. The changes make it simple to get info and look at it. This helps us learn more about how the brain works. You can also always keep an eye on your brain with apps on your phone and other tech.
Potential for Prevention and Early Intervention
These days, new tools have changed the way we study the brain in big ways. These changes have made it easy for us to get and look at statistics. We learn more about the brain from this. As you age, real-time phone apps and tech that you wear can also help you keep an eye on your brain health.
People who think this way should work out, make friends, and eat well every day. Getting help early not only makes brain health better, but it also makes people more likely to be involved in their own care. If you do a few easy things every day, your brain will stay healthy as you get older.
Conclusion
Even though aging can have a wide range of affects on a person’s brain, it is essential to comprehend these consequences if you want to preserve your cognitive health as you age. Numerous changes could happen to your memory, cognitive speed, and emotional control, to name a few. Because you are aware of the impacts of aging effects on the brain, you may take proactive steps to support its health.
Mental exercises, social interaction, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are some ways you can support your aging effects on the brain.
Related topics
- Best 7 Health Benefits Of Exercise
- 4 Best Exercises for Health
- 12 Best Supplements for Skin Health
- 8 Effective Habits to Boost Mental Clarity and Focus
- Fuel Your Body Right: 6 Best Ultimate Guide to Smart Nutrition
- Home




































































































